|

VISJET3
¾ Real-time Hydro-environmental Modeling and
Visualization
System for Public Engagement
實時水環境模擬和可視化系統
Supported by Innovation and Technology Fund (ITF)
- Innovation and Technology Support Programme (ITSP) - Project
ITS/071/06
Principal Investigators:
Prof. JHW Lee and
Dr. WP Wang, The University
of Hong Kong
Summary
Environmental sustainability is critical to the economic development
of Hong Kong and the Pearl River Delta; it can only be achieved with the aid of reliable
decision support tools. In particular, quantitative impact assessment plays an important role in
the sustainable development of our coastal and marine resources. A robust
three-dimensional (3D) environmental modelling system is needed to predict the impact of
accidental or steady pollution sources on sensitive receivers (mangroves, fish culture zones,
coral beds, sea water intakes, beaches).
This proposal is a joint venture of the Croucher Laboratory of
Environmental Hydraulics
and the Computer Graphics Laboratory of the University of Hong Kong. The
objective is to develop a cutting-edge real time environmental modeling and visualization system,
called VISJET3,
that will enable effective and scientifically advanced impact and risk assessment. The
unique technology will enable robust and seamless 3D environmental impact prediction from
the near to the far field, and effective communication and public engagement. This pilot
applied research will pave the way for a real time environmental modeling and
visualization system for the entire Hong Kong and regional waters - with significant benefit for real
time water quality forecasts and environmental management.
環境的保持對香港及珠江三角洲的經濟發展至為關鍵,而實現這個目的有賴於可靠的決策工具。特別對於海岸及海洋資源的可持續發展,量化的環境評估更扮演重要的角色。我們需要一個魯棒(robust)的三維環境模擬系統來預測因意外或持續的污染排放而產生的環境影響(如對紅樹林、海魚養殖區、珊瑚、取水口、海灘)。
本項目由香港大學裘槎水力實驗室和圖型學實驗室聯合提出。項目的主旨是發展一個尖端的實時環境模擬及可視化系統
(VISJET3),可作有效及先進的環境影響及危機評估。這個獨特的科技可提供魯棒的三維環境影響預測,近場到遠場亦可同時處理,並透過簡明的方式讓公眾可參與其中。這個前瞻性的應用研究將會發展為一個覆蓋全港水域的實時環境模擬及可視化系統
¾ 對推動實時水質預測及環境管理有重大意義。
Objectives
Worldwide there is currently no robust model for satisfactory risk
assessment and effective communication of
environmental impact to the stakeholders. Despite the increasing
computing power and advances in hydrodynamic
and water quality modelling, current methods of impact
assessment suffer from several major drawbacks.
For environmental risk assessment it is necessary to predict the
impact of effluent discharges for a wide range
of discharge and ambient conditions. For many densely populated coastal
cities in China and other Asian Pacific countries, this
prediction poses particular technical challenges. The effluent discharges are typically located in relatively
shallow waters of 5-20 m depth, close to
sensitive receivers such as beaches or fisheries. Hence impact
assessment tools must be able to cater for
both the near field and the far field. Current industry-standard
models cater for only the near field or only the far field. For
example, the USEPA plume model gives
predictions of pollutant concentrations only in the initial mixing zone.
In addition, the model cannot provide
satisfactory predictions for buoyant jets with three-dimensional
trajectories; hence risk assessment over a wide spectrum of
discharge and ambient conditions is not
possible.
On the other hand, 3D far field hydrodynamic models such as Delft3D
can resolve only the far field. Predictions
tend to be overly optimistic as the impact is averaged over a region at
least of the order of 100 m. Despite the
advances in environmental transport modeling, the coupling of
the near and intermediate/far field prediction methods is still
not resolved. For many practical situations,
the use of either the near field model or the far field model alone is
highly unsatisfactory. In addition, the lack
of an effective visualization technology integrated with the
simulation engine renders it difficult for the stakeholders to
appreciate environmental impact by poring
through voluminous simulation data or static charts and figures.
The objective of this project is to develop a GIS-based and
integrated hydraulic-virtual reality (VR)
system, called VISJET3, that will enable effective and scientifically advanced impact and
risk assessment. The technology will enable (i)
robust and seamless 3D environmental impact prediction from
near to the far field; (ii) full integration with GIS data and
advanced visualization capability; (iii) interactive internet access; and (iv) effective communication and public
engagement.
Sponsoring Organizations
Environmental Protection Department, HKSAR 香港特別行政區政府環境保護署
Drainage Services Department, HKSAR 香港特別行政區政府渠務署
Maunsell Environmental Management Consultants Ltd. 荗盛環境管理顧問有限公司
Movies
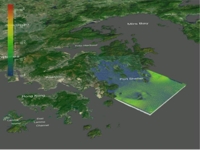 |
This movie shows the environmental impact of
a simulated outfall discharge in the Port Shelter. (6.18 MB) |
 |
This movie shows the comparison of E.
coli concentrations due to the HATS outfall with and without
disinfection. (17.3 MB) |
Publications
-
Lee, J.H.W. and Choi, K.W., (2008).
"Real-time hydro-environmental modeling and visualization system for
public engagement", Environmental Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 8, pp. 411-421.
[pdf 519KB]
-
Wong, K.T.M. Wong, Lee, J.H.W. and Hodgkiss, I.J.,
(2007). "A Simple Model
for Forecast of Coastal Algal Blooms", Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science,
Vol. 74, No. 1-2, pp. 175-196. [pdf
1.06MB]
-
Lai, A.C.H., Yu, D. and Lee, J.H.W., (2007), "Near and
Intermediate Field
Mixing of a Rosette Jet Group", Proc. Fifth International Symposium on
Environmental Hydraulics, Dec. 4-7, 2007, Tempe, Arizona, USA (CD-ROM).
[pdf 260KB]
-
Choi, K.W. and Lee, J.H.W., (2007), "Distributed
Entrainment Sink Approach
for Modelling Mixing and Transport in the Intermediate Field", Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE,
Vol. 133, No. 7, pp. 804 - 815. [pdf
668KB]
-
Choi, K.W. and Lee, J.H.W., (2007), "Distributed
Entrainment Sink Approach
(DESA) - a New Method for Modelling Mixing and Transport in the Intermediate
Field", Report No. CEHL-R07-01, Croucher Laboratory of Environmental
Hydraulics, Department of Civil Engineering, The University of Hong Kong.
[pdf 3.1MB]
 Also check here for more details on
the DESA technology.
Also check here for more details on
the DESA technology.
VISJET
Publications
-
Lee, J.H.W., Wang, W.P., Cheung, V., Kuang, C.P., Choi,
D.K.W., Tu, C.H.,
Chan, B., and Choi, Y.K., (2003), "VISJET and VISFLOOD: software for
environmental hydraulic modeling and visualization", Proc. 7th Asian
Symposium on Visualisation, Nov.3-7, 2003, Singapore (CDROM). [pdf
1.36MB]
-
Lee, J.H.W., Cheung, V., Wang, W.P., and Cheung,
S.K.B., (2000), "Lagrangian
modeling and visualization of rosette outfall plumes", Proc.
Hydroinformatics 2000, Iowa, July 23-27, 2000 (CDROM). [pdf
595KB]
Technical Notes
Tutorial Cases
 Click here to download all six
tutorial cases.
Click here to download all six
tutorial cases.
VISJET simulates the mixing of single or multiple
buoyant jets discharged from one or more risers mounted on an ocean
outfall. In a particular application, the input parameters for the ambient
condition, the outfall, riser, and jet characteristics are needed. For
example, a single buoyant jet can be modelled by specifying a single jet
on a single riser. Multiple jets can be simulated by specifying a single
jet on each of a number of risers. Rosette jet groups on multiple risers
can be simulated by specifying the multiple jet characteristics on each of
the risers.
In VISJET3, jet discharges are simulated against a real 3D background of
the Hong Kong topology, in which the discharge and the topology can be
viewed at any orientation. In this way the environmental impact to nearby
sensitive receivers can easily be visualized and assessed. In this series
of tutorials, we will illustrate this can be done step by step, starting
from the simple case of a single buoyant plume discharge, to a more
complicated discharge of a rosette jet group, and finally end with a real
outfall located in Sai Kung.
-
Tutorial 1 - Buoyant jet in unstratified stagnant
fluid/crossflow. [pdf 35.4KB]
-
Tutorial 2 - Buoyant jet in stratified stagnant fluid/crossflow
with a riser. [pdf 70.6KB]
-
Tutorial 3 - An example outfall in the Port Shelter. [pdf 27.0KB]
-
Tutorial 4 - Discharge of rosette jet groups from multiple risers :
the HATS Outfall. [pdf 24.0KB]
-
Tutorial 5 - Round buoyant jet in a confined region - dynamic coupling
of jet and surrounding fluid. [pdf
72.0KB]
-
Tutorial 6 - Environmental impact assessment for Sai Kung Sewage
Treatment Works (SKSTW) Outfall. [pdf
284KB]
Software
Download
 Click here to download
VISJET 3 installation file visjet30_setup.exe
(76.4MB).
Click here to download
VISJET 3 installation file visjet30_setup.exe
(76.4MB).
This version of VISJET is provided for
non-commercial use only. Note that VISJET 3.0 does not currently
support 64-bit operating systems such as Windows XP 64-bit and
Windows Vista 64-bit.
System Requirements
PC with 1 gigahertz or higher processor clock speed; 2 gigahertz or
above recommended for far-field simulation.
Supports Microsoft Windows 2000, Microsoft Windows XP, and Microsoft
Windows Vista.
512 megabytes (MB) of RAM minimum supported; 1 gigabytes (GB) or more
recommended, depends on data file size.
300 megabytes (MB) of available hard disk space.
SXGA (1280x1024) or higher-resolution video adapter and monitor.
Graphics card with 128 megabytes (MB) video memory. Integrated
graphics chips such as Intels GMA 950 and GMA X3000 graphics are not
supported. Nvidias GeForce 6 series or above recommended.
Keyboard and scroll mouse or compatible pointing device.
 Click here to
download
tutorial 6's project files (1.0GB), which are not included in VISJET 3
installation
file
due to its size.
Click here to
download
tutorial 6's project files (1.0GB), which are not included in VISJET 3
installation
file
due to its size.
|